Preguntar la hora:
Estas son unas opciones para preguntar la hora en inglés:1. What time is it?
2. What’s the time?
3. Have you got the time?
DEFINING AND NON-DEFINING RELATIVE CLAUSES
 |
| Read +info |
The present perfect is used to indicate a link between the present and the past. The time of the action is before now but not specified, and we are often more interested in the result than in the action itself.
| Grados | Uso | Ejemplos |
|---|---|---|
| Positivo | Es el grado más simple. Designa una cualidad del objeto/persona. | Peter is a happy boy (Pedro es un chico feliz) |
| Comparativo | Compara dos elementos. Puede ser de igualdad, de inferioridad o de superioridad. | A happier boy (Un chico más feliz) |
| De igualdad. Iguala dos elementos. | Mary is as happy as Peter (María es tan feliz como Pedro) | |
| De inferioridad. Un elemento posee la cualidad en menor grado. | Mary is not as happy as Peter (María no es tan feliz como Pedro) | |
| De superioridad. Un elemento posee la cualidad en menor grado. | Mary is happier than Peter (María es más feliz que Pedro) | |
| Superlativo | Compara dos elementos en su grado máximo. Destaca la cualidad de un elemento sobre los demás. | Mary is the happiest girl in the class (María es la chica más feliz de la clase) |
| Adjetivo | Comparativo | Superlativo |
|---|---|---|
| good | better | best |
| bad | worse | worst |
| far | farther/further | farthest/furthest |
| little | less | least |
| much/many | more | most |
ED - ING
Estructura:
Este condicional tiene dos partes: “la condición” y “el resultado”. Observa los siguientes ejemplos:
-If you come to the party, you will meet my sister. (Si vienes a la fiesta, conocerás a mi hermana)
-If she gets home late, I will be very angry. (Si ella llega a la casa tarde, estaré muy enejado)
La condición:
El tiempo verbal que utilizamos para la oración condicional es el presente simple -“you come” y “she gets”- (Para mayor información sobre este tiempo verbal puedes ir a la lección sobre el presente simple en inglés)
El resultado:
Estas frases utilizan el futuro con WILL acompañando de la FORMA BASE DEL VERBO -“will meet” y “will be”-. (Puedes ir a la lección sobre el futuro con WILL)
Recuerda:
Podemos cambiar el orden de la oración sin alterar el significado:
I will help you if I have time. (Te ayudaré si tengo tiempo)
Podemos usar los verbos modales CAN o MAY en lugar de WILL; ejemplos:
-If I don’t have to work on Saturday, we can go to the cinema. (Si no tengo que trabajar el sábado, podemos ver una película)
-If she studies hard for the exam, she may get a good grade. (Si ella estudia dura para el examen, puede que obtenga una buena calificación)
Ahora, ya puedes visitar la sección "Homework" y ponerte a prueba con los ejercicios.
PERSONAL PRONOUNS + POSSESSIVES
Sujeto | Pronombre Posesivo |
I | Mine (Mío) |
You | Yours (Tuyo) |
He | His (Suyo-de él) |
She | Hers (Suyo- de ella) |
It | Its (Suyo- neutro) |
We | Ours (Nuestro/a) |
You | Yours (Vuestro/a) |
They | Theirs (De ellos) |
Sujeto | Adjetivo Posesivo | Pronombre Posesivo |
I | My (Mi) | Mine (Mío/a) |
You | Your (Tu) | Yours (Tuyo/a) |
He | His (Su-de él) | His (Suyo/a-de él) |
She | Her (Su- de ella) | Hers (Suyo/a- de ella) |
It | Its (Su- neutro) | Its (Suyo- neutro) |
We | Our (Nuestro/a) | Ours (Nuestro/a) |
You | Your (Vuestro/a) | Yours (Vuestro/a) |
They | Their (De ellos) | Theirs (De ellos) |
EXPRESSING THE FUTURE
(WILL - GOING TO - PRESENT CONTINUOUS)
 | |
| Title: "Handling Incoming Mail" | |
| • Content: Begin by explaining the significance of organized mail handling in an office environment. Share that efficient mail handling is crucial for maintaining business operations and … | |
|
El pasado simple se utiliza para referirse a acciones que se completaron en un período de tiempo anterior al presente. En el pasado simple, el proceso de realizar la acción no es importante. Lo que importa es que la acción se completó en el pasado. La acción pudo haber sido en el pasado reciente o hace mucho tiempo.
Entonces, comencemos a aprender el Pasado Simple, uno de los tiempos más comunes al hablar en inglés, aquí te presentamos algunos puntos que debes prestar mucha atención.
USO DEL SIMPLE PAST
I saw a movie last week.
I finished work, walked to the beach and met my friends.
I lived in Italy for five years.
I often played football when I was a young man.
Forming the Simple Past
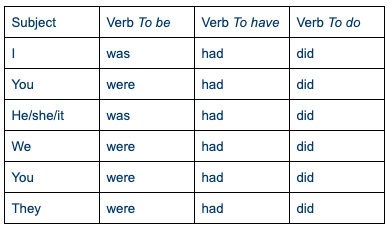
Oraciones afirmativas en pasado simple
En oraciones afirmativas, el orden de las palabras es sujeto + verbo y la forma del verbo en pasado simple es la misma para todos los sujetos (with the exception of ‘to be’ – was/were).
Subject + past simple + object
Por ejemplo:
I played football yesterday.
He saw his family last week.
I was in France in June.
GIVING DIRECTIONS
 | |
| UNIT 1 – WHO’S WHO IN THE OFFICE | |
| Lesson Plan: Business English - Company Protocols and Visitor Reception | |
|
CARDINAL AND ORDINAL NUMBERS
Cardinal numbers are primary numbers – that means that they show how many of something there are. These cannot be fractions or decimals, but have to be whole, counting numbers. These include one, two, three, four, five, six, etc.
Ex. Charlie has two (2) cats.
Ordinal Numbers
An ordinal number is used to show the order of something, or the place of that thing in a list. These include first (1st), second (2nd), third (3rd), fourth (4th), fifth (5th), sixth (6th), etc.
- Copyright © 2025 SopebiAntonio - Date A Live - Powered by Blogger - Designed by Johanes Djogan -